Unified Namespace
Unified Namespace in Manufacturing: The Digital Backbone of Industry 4.0
By: Destiny Dickerson
The manufacturing industry is undergoing significant changes thanks to new technologies like the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), machine learning, and automation. As more systems become connected, it’s crucial to organize and manage data effectively. That’s where the Unified Namespace (UNS) comes in—it’s quickly becoming a key part of digital transformation in manufacturing.
What is a Unified Namespace?
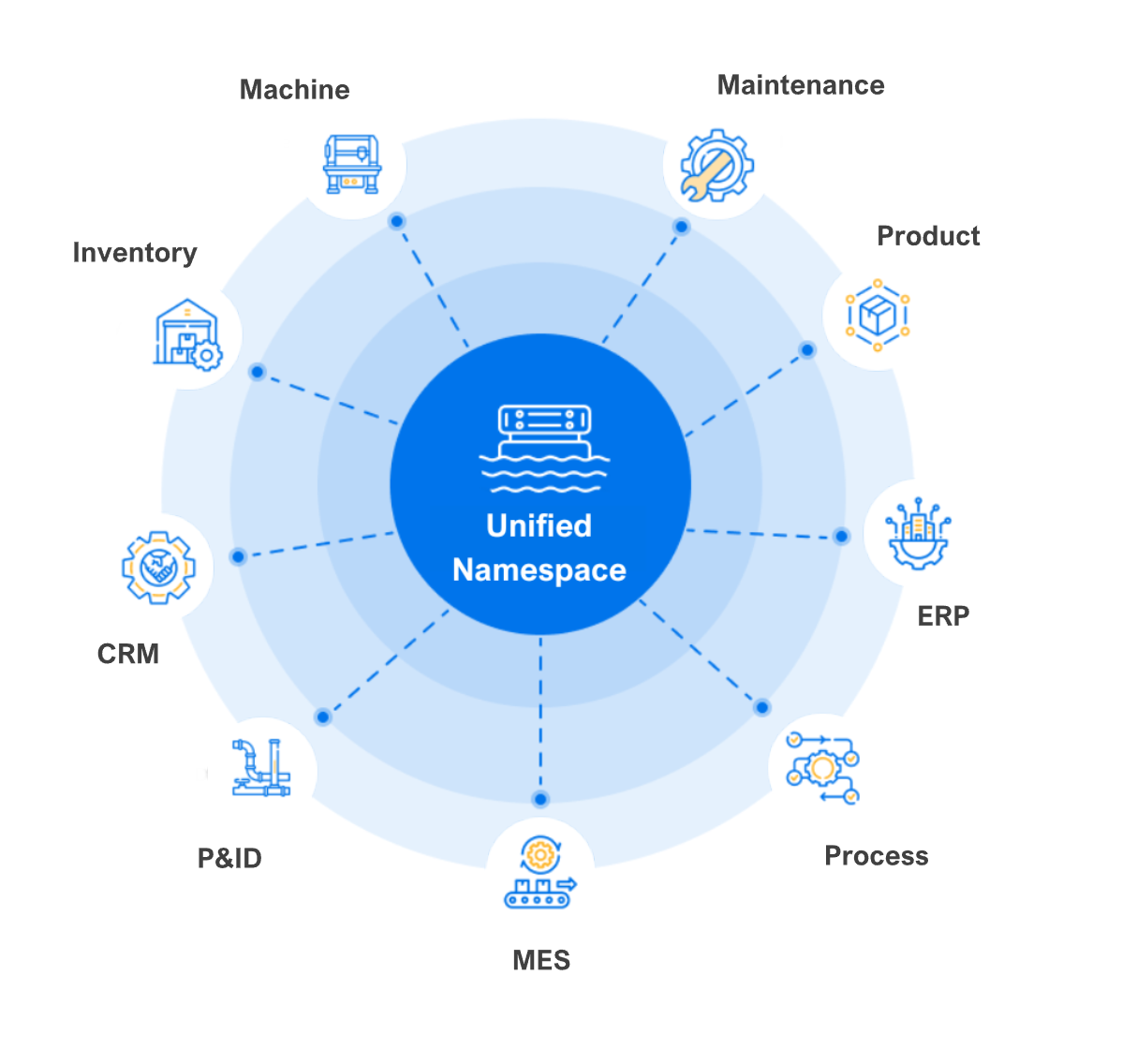
A Unified Namespace is like a central digital library where all manufacturing data lives. It gathers real-time data from both factory equipment (Operational Technology, or OT) and business systems (Information Technology, or IT), and organizes it in one easy-to-access space. Unlike older systems that were closely linked and hard to change, a UNS is flexible and allows systems to communicate without being directly connected.
The data is usually shared using the MQTT protocol, which is lightweight and ideal for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). The data is organized in a structured way, similar to file folders. For example:
factory1/line1/machine3/temperature
This setup makes it easy to manage and scale, whether you have one facility or multiple sites.
Why Manufacturing Needs a Unified Namespace
Many manufacturing systems are outdated and work separately, making it hard to share data. A Unified Namespace solves this by acting as the brain of the operation, where all data moves freely and securely.
1. Real-Time Updates
Systems can instantly get new data, helping with real-time decisions, predictive maintenance, and quick reactions to issues.
2. Breaks Down Data Silos
By combining OT and IT data in one place, everyone has a full view of operations, making teamwork and decision-making easier.
3. Easy to Expand
New tools or machines can be added without having to redo the entire system.
4. Standardization
It creates a common language for all systems, even across different factories or vendors.
5. Simplified Integration
Using a publish/subscribe model, systems can join or leave without disrupting others, reducing complexity and cost.
Key Parts of a Unified Namespace
-
MQTT Broker: This handles real-time messages between devices and systems. Examples include HiveMQ, Mosquitto, and EMQX.
-
Topic Hierarchy: A clear structure that mirrors the plant layout, like
site1/packaging/line2/machine7/status. -
Edge Devices: These connect old machines to the UNS and convert their signals to be compatible with MQTT.
-
Security: Since all data flows through the UNS, strong encryption, user controls, and security measures are essential.
Real-World Example: A Beverage Factory
Imagine a drink factory with separate stations for bottling, labeling, and packing. Usually, each system might send data to a different place, causing delays. With an UNS (Unified Namespace), all stations send their data to a single location. A dashboard can monitor temperatures and flow rates. If there’s a labeling error, a quality control system gets notified immediately. Maintenance teams can also monitor equipment data and respond to issues early. This setup improves speed, reduces downtime, and ensures better quality.
Challenges to Keep in Mind
-
Standardization: Everyone must agree on how to name and organize topics.
-
Old Equipment: Many older machines need special tools (edge devices) to connect to the UNS.
-
Cultural Resistance: Moving from isolated departments to a shared system may face pushback.
-
Cybersecurity: More connected systems mean stronger security is a must.
UNS and Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is all about blending digital tools with physical operations. To make this work, you need a strong data system where machines, software, and people can interact. The UNS makes that possible, supporting real-time insights and smooth collaboration. Technologies like AI, digital twins, and smart supply chains all depend on the kind of clean, real-time data that the UNS provides.
Final Thoughts
The Unified Namespace isn’t a product—it’s a strategy. It changes how manufacturers think about data: not as scattered or delayed, but as unified and immediate. As more companies go digital, UNS will be at the heart of innovative, scalable, and responsive operations. For manufacturers aiming to stay competitive, embracing UNS isn’t just helpful—it’s essential.
Sources
- Reynolds, W. (n.d.). What is a Unified Namespace? Intellic Integration. Retrieved from https://www.intellicintegration.com
- HiveMQ. (n.d.). MQTT and Unified Namespace for Industry 4.0. Retrieved from https://www.hivemq.com
- Inductive Automation. (n.d.). The Role of MQTT in IIoT Architectures. Retrieved from https://inductiveautomation.com
- ARC Advisory Group. (n.d.). Digital Transformation in Manufacturing. Retrieved from https://www.arcweb.com
- Photo by SymphonyAI. (n.d.). Unified Namespace Diagram. Retrieved from https://www.symphonyai.com/wp-content/uploads/UNS-8.svg