Self-healing materials in Manufacturing
A Future Fueled by Resilience
By: Destiny Dickerson
What Are Self-Healing Materials?
Self-healing materials are engineered substances designed to repair themselves after damage, eliminating the need for human intervention. Inspired by biological systems, such as how skin heals after a cut, these materials utilize embedded mechanisms, including microcapsules, vascular networks, or chemical reactions, to restore their original properties. In manufacturing, this innovation translates to longer product lifespans, reduced downtime, and lower maintenance costs.
How They Work in Manufacturing
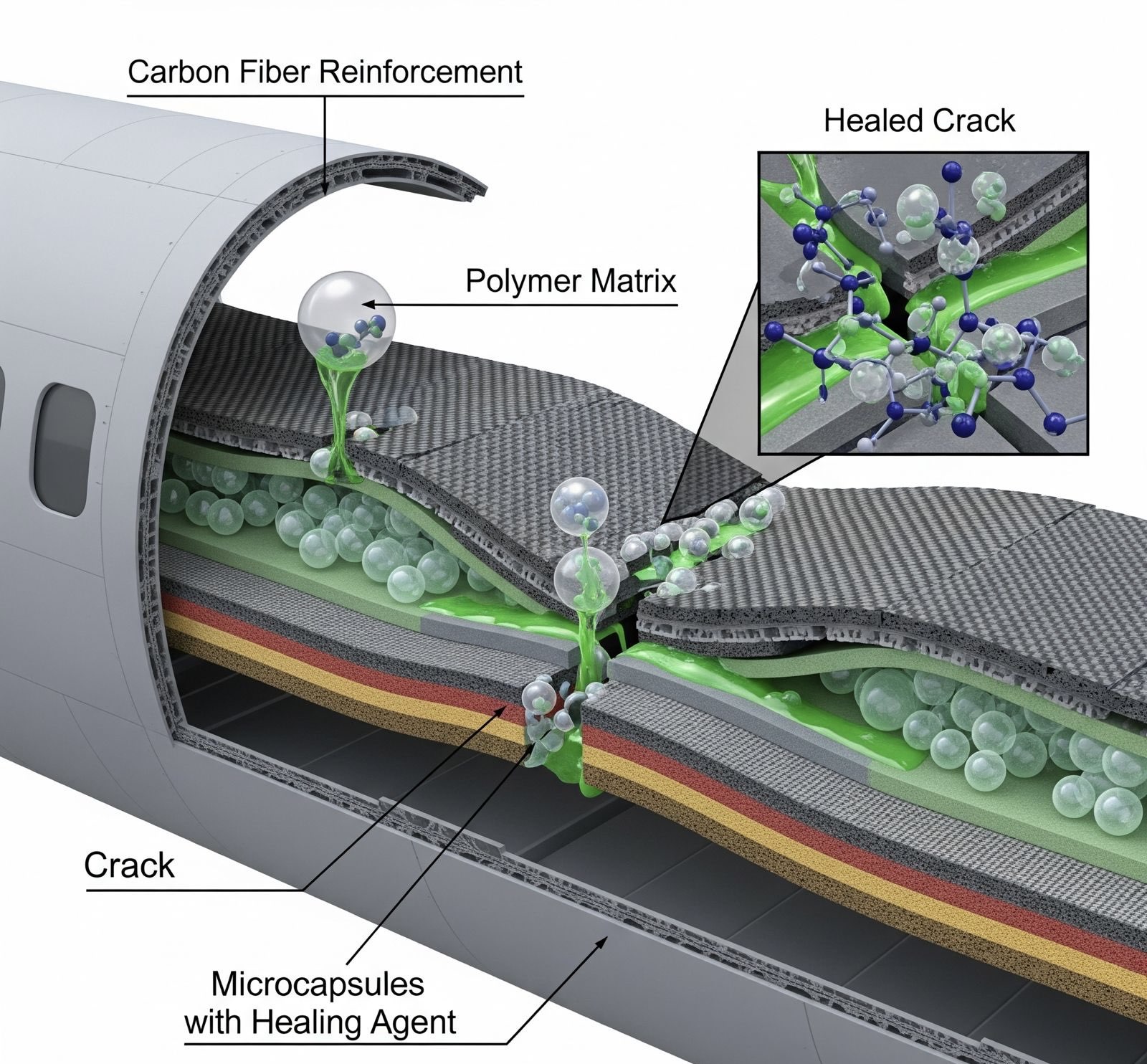
When cracks or wear appear in traditional materials, the damage typically grows until failure occurs. Self-healing materials interrupt that cycle. For example, some polymers release a healing agent stored in microcapsules when a fracture occurs. The agent flows into the crack and hardens, effectively repairing the damage. In other cases, heat or light can trigger healing responses in coatings or composites. This ability to automatically address wear and tear reduces the frequency of repairs and enhances production efficiency.
Real-World Applications
The promise of self-healing materials is already being tested across multiple industries. In aerospace manufacturing, lightweight composites that can self-heal improve aircraft safety and reduce maintenance costs. Automotive manufacturers are exploring self-healing paints that eliminate minor scratches, reducing the need for costly refinishing. Even in electronics, self-healing circuits are being developed to extend device lifespans and minimize electronic waste. These examples illustrate how manufacturing is gradually transitioning toward more sustainable and resilient solutions.
The Benefits for Manufacturers
For manufacturers, the adoption of self-healing materials could transform operations. Reduced downtime means production schedules remain consistent, while longer-lasting products reduce warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction. Additionally, by minimizing waste and extending product life cycles, self-healing materials support sustainability initiatives, a growing concern in modern manufacturing.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the promise, challenges remain. Scaling the production of self-healing materials is expensive, and ensuring they perform reliably under diverse industrial conditions remains a research priority. Manufacturers will need to balance costs with long-term benefits before these materials can be widely implemented.
The Future of Manufacturing with Self-Healing Materials
As research advances, the integration of self-healing materials could redefine how products are designed, produced, and maintained. Instead of reacting to failures, manufacturers will be able to create systems that prevent them from occurring. This shift aligns with broader trends in smart manufacturing, where predictive technologies, automation, and advanced materials converge to make factories more resilient and efficient.
Sources
- National Library of Medicine – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- ScienceDirect – https://www.sciencedirect.com
- MIT Technology Review – https://www.technologyreview.com
- Nature – https://www.nature.com