MQTT
Understanding MQTT and Its Role in IoT for Manufacturing
By: Destiny Dickerson
In today’s fast-changing manufacturing world, the Internet of Things (IoT) transforms factory operations through more intelligent automation and real-time data exchange. MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is the center of this shift, a lightweight messaging protocol built for fast, reliable communication between connected devices. Although it was initially designed in the late 1990s for remote monitoring of oil pipelines, MQTT is now a preferred standard in industrial environments where bandwidth is limited and uptime is critical.
What is MQTT?
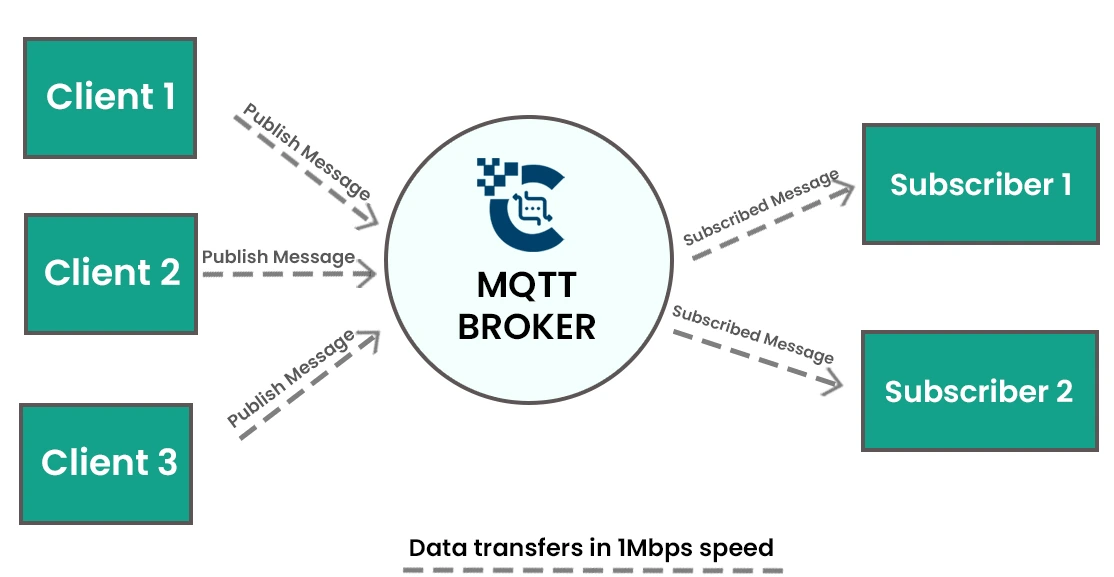
MQTT is based on a publish-subscribe model. Devices (clients) send messages to a central broker, which then distributes those messages to other devices that have subscribed to the relevant topics. This design reduces network traffic and allows efficient, real-time data sharing—even over unreliable or low-bandwidth connections.
Key Features:
- Lightweight Design – Suitable for devices with limited computing power.
- Efficient Bandwidth Usage – Only essential data is transmitted.
- Flexible Quality of Service Levels – Delivery can be guaranteed depending on need.
- Last will (LWT) – Alerts the network if a device disconnects unexpectedly.
Why MQTT Works Well in Manufacturing
Smart factories generate enormous amounts of data through sensors, machines, and systems. MQTT offers a streamlined way to manage this complexity while enabling reliable, scalable communication.
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Factories use MQTT to monitor equipment performance and environmental conditions instantly. A temperature sensor, for example, can send data that immediately triggers a response, such as sounding an alarm or stopping machinery if unsafe conditions are detected.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Instead of waiting for something to break, manufacturers can monitor equipment for early warning signs. Data such as vibration or pressure readings can indicate issues before they lead to failure, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing costly downtime.
3. Production Line Optimization
MQTT enables better coordination across machines and workstations. If a delay is detected in one part of the line, upstream machines can adjust speed automatically, preventing overproduction or system congestion.
4. Remote Operations
Because MQTT is efficient and adaptable, it’s ideal for remote monitoring and control. Engineers can view real-time data and manage operations from any location, which is especially valuable in large or hazardous manufacturing environments.
Integration with Cloud and Edge Systems
MQTT integrates easily with popular cloud platforms, enabling manufacturers to apply artificial intelligence, analytics, and automation to improve decision-making. It also works well in edge computing scenarios, where local gateways filter and process data before sending only relevant information to the cloud, reducing latency and bandwidth use.
Security in MQTT for Manufacturing
Security is essential in any industrial setting. While MQTT is simple and efficient, it supports strong protections such as encryption, device authentication, and access controls. These features ensure that only authorized users and systems can interact with the data, keeping sensitive operations secure.
Conclusion
MQTT plays a key role in enabling smart, connected manufacturing. Its speed, flexibility, and low overhead make it ideal for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and system-wide automation. As factories continue embracing digital transformation, MQTT will remain a core technology powering the future of industrial IoT.
Sources
- AWS. “MQTT.” Amazon Web Services. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/iot/latest/developerguide/mqtt.html
- Eclipse Mosquitto. “MQTT Documentation.” https://mosquitto.org/
- HiveMQ. “MQTT Use Cases in Industrial IoT.” https://www.hivemq.com/blog/
- IBM Developer. “MQTT – The Standard for IoT Messaging.” https://developer.ibm.com/articles/iot-mqtt-why-good-for-iot/
- Microsoft. “MQTT Support in Azure IoT Hub.” https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-hub/iot-hub-mqtt-support
- OASIS. “MQTT Version 3.1.1 Plus Errata 01.” https://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v3.1.1/os/mqtt-v3.1.1-os.html
- TechTarget. “MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport).” https://www.techtarget.com/iotagenda/definition/MQTT-Message-Queuing-Telemetry-Transport
- Photo by Bevywise for Manufacturing Solutions - Bevywise MQTT Use cases. (n.d.). Www.bevywise.com. https://www.bevywise.com/mqtt-usecases/manufacturing-solutions.html