Green Manufacturing
Building a Sustainable Future One Factory at a Time
By: Destiny Dickerson
In today’s rapidly changing world, sustainability has evolved from a trendy concept into an essential part of global industry. As climate change intensifies and natural resources become increasingly scarce, businesses across all sectors are being called upon to reduce their environmental impact. Manufacturing, a sector traditionally associated with high energy consumption and waste, is undergoing a significant transformation through the adoption of green manufacturing technologies.
What is Green Manufacturing?
Green manufacturing refers to the creation of products through processes that minimize negative environmental impacts, conserve energy and natural resources, and promote sustainability throughout the entire production cycle. It encompasses everything from cleaner production methods to the use of environmentally friendly materials and energy sources. The aim is to achieve economic growth without sacrificing the health of the planet.
Key Technologies Driving Green Manufacturing
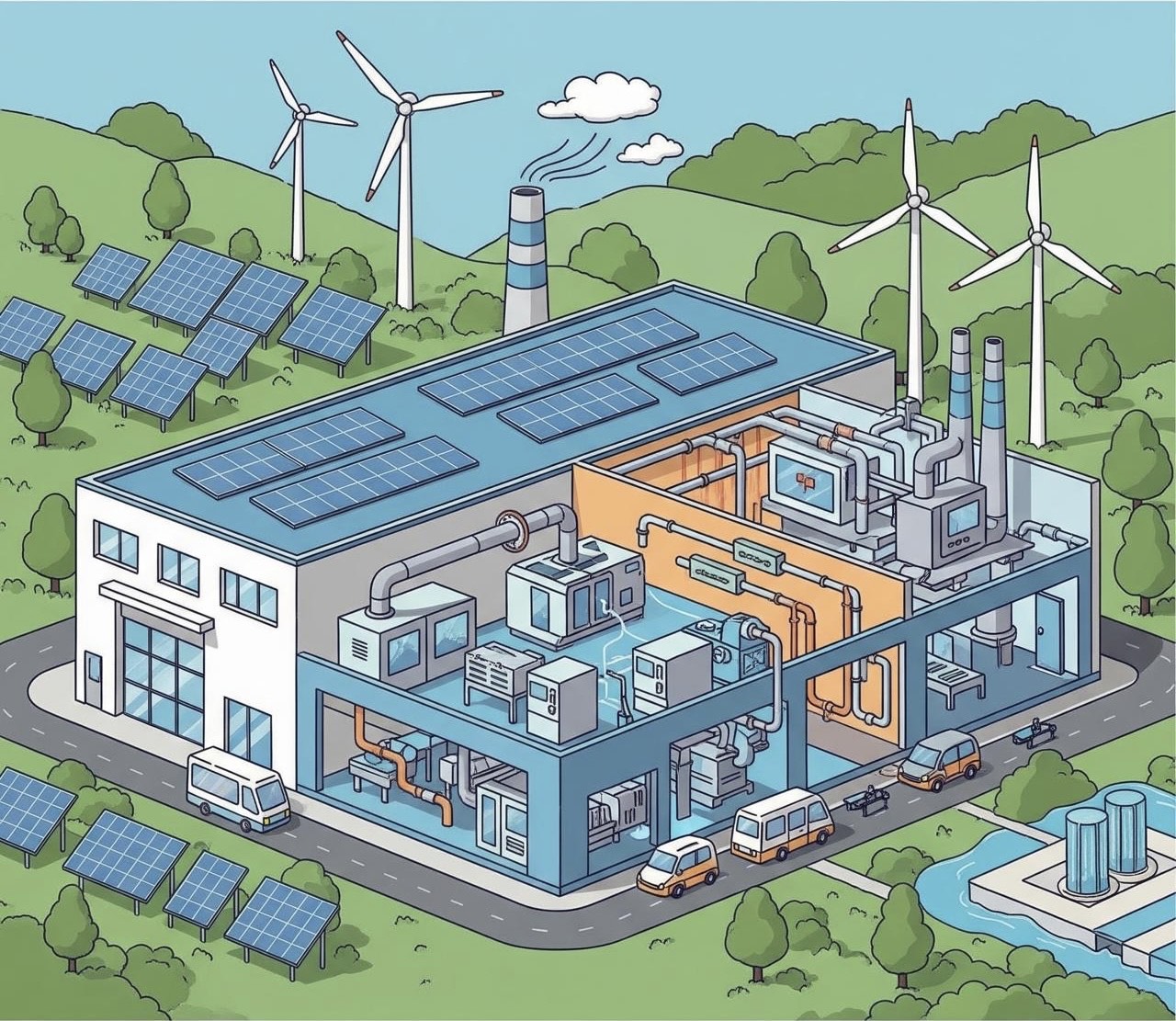
Energy-Efficient Machinery
One of the foundational elements of green manufacturing is the use of energy-efficient equipment. Traditional manufacturing machines consume significant amounts of electricity and often operate inefficiently. In contrast, modern machinery features include variable frequency drives, automatic shut-off systems, and intelligent monitoring tools, which collectively reduce energy consumption. These upgrades lower operating costs while reducing carbon emissions.
Renewable Energy Integration
Many manufacturing facilities are transitioning toward renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydropower. Incorporating these sources helps manufacturers reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and cut greenhouse gas emissions. Some companies install on-site renewable systems, while others purchase clean energy from utility providers. This transition is not only environmentally responsible but also shields businesses from fluctuations in fossil fuel prices.
Waste Heat Recovery
Manufacturing processes often generate large amounts of waste heat. Rather than letting this energy go unused, waste heat recovery systems capture and repurpose it for heating buildings, preheating materials, or generating electricity. This technology can significantly improve overall energy efficiency and contribute to more sustainable operations.
Closed-Loop Manufacturing
Also known as circular manufacturing, closed-loop systems aim to eliminate waste by reusing materials within the production cycle. Instead of discarding scrap or defective products, materials are recovered, remanufactured, or recycled for reuse. This approach reduces the demand for raw materials, minimizes landfill waste, and helps manufacturers comply with environmental regulations.
Sustainable Materials
Choosing sustainable materials is a critical part of green manufacturing. Companies are increasingly turning to biodegradable plastics, recycled metals, organic textiles, and responsibly sourced wood. Using environmentally friendly materials reduces the ecological footprint of the final product and supports broader efforts to reduce pollution and resource depletion.
Digital Technologies and AI Optimization
Advanced digital tools are revolutionizing how manufacturers optimize their operations. Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and digital twins enable manufacturers to simulate production lines, identify inefficiencies, and optimize performance before implementing changes on the ground. These innovations help conserve energy and materials while boosting productivity.
The Business Case for Green Manufacturing
Investing in green technologies is not just about environmental responsibility—it also makes good business sense. Energy-efficient systems and waste-reduction strategies often lead to substantial cost savings over time. Furthermore, adopting sustainable practices can improve a company’s reputation, attract eco-conscious consumers, and help businesses comply with evolving environmental regulations.
Green manufacturing also prepares companies for the future. As governments implement stricter climate policies and consumers demand cleaner products, manufacturers that have already embraced sustainability will be better positioned to adapt and thrive.
Real-World Example: Siemens
Siemens, a global leader in technology and manufacturing, exemplifies what green manufacturing looks like in practice. The company operates multiple carbon-neutral factories and has integrated AI and IoT technologies to monitor and improve energy efficiency. Siemens has also committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions across its global operations by 2030. Their example demonstrates that large-scale industrial operations can embrace sustainability without compromising innovation or profitability.
Conclusion
Green manufacturing technologies are revolutionizing the way products are made in the 21st century. By investing in cleaner, more efficient systems and materials, manufacturers can reduce their environmental impact, cut costs, and build stronger relationships with customers and communities. As technological advancements continue to emerge, green manufacturing will play a central role in creating a sustainable industrial future.
Now is the time for manufacturers to lead by example, demonstrating that economic growth and environmental stewardship are not mutually exclusive but are, in fact, mutually reinforcing.
Sources:
- U.S. Department of Energy. (2020). Energy Efficiency in Industry. https://www.energy.gov/eere/amo/energy-efficiency-industry
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). (2023). Renewable Energy and Industry. https://www.irena.org
- Siemens AG. (2023). Sustainability in Manufacturing. https://www.siemens.com/global/en/company/sustainability.html
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (2022). Sustainable Manufacturing. https://www.epa.gov/sustainability/sustainable-manufacturing
- Deloitte Insights. (2023). The Smart Factory and Industry 4.0. https://www2.deloitte.com