Digital Twins
From Concept to Reality: Implementing Digital Twins in Manufacturing
By: Destiny Dickerson
Introduction
We’re now in the fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, which is bringing significant changes to how things are made around the world. One of the leading tools in this shift is the digital twin.
A digital twin is more than just a copy of something—it’s a live, data-driven version of a real object, process, or system. When used correctly, digital twins can transform how products are made, how efficient factories run, and how machines are maintained. This article examines how manufacturers can transition from theory to real-world applications of this technology.
What Is a Digital Twin?
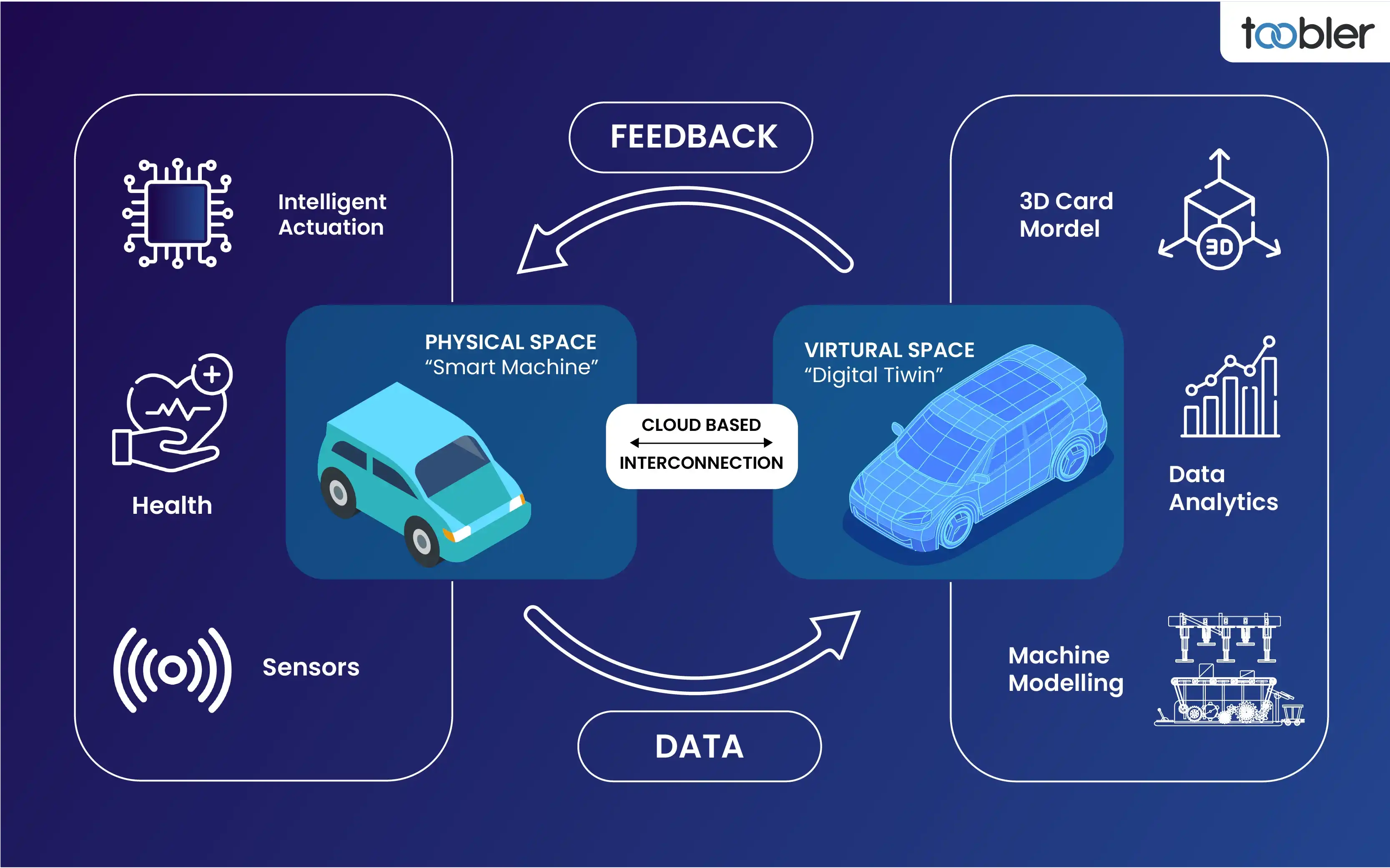
A digital twin is a virtual version of a real object that updates in real-time using data from sensors and connected devices. By combining technologies like machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, it reflects any changes happening to its physical counterpart.
First introduced by Dr. Michael Grieves in the early 2000s, digital twins gained popularity alongside advancements in IoT, cloud computing, and edge technology. Today, they are key tools in smart factories and modern production systems.
Benefits of Digital Twins in Manufacturing
-
Real-Time Insights – Manufacturers can constantly monitor equipment and production, quickly spotting and fixing inefficiencies.
-
Predictive Maintenance – Live data helps predict when machines might break down, allowing for early repairs and fewer disruptions.
-
Faster Product Design – Products can be tested and improved virtually before being physically built, speeding up development and cutting costs.
-
Cost Savings – Digital twins can help save energy, reduce waste, and streamline supply chains.
-
Better Quality Control – They can quickly detect and fix quality issues, resulting in fewer defects.
How to Set Up Digital Twins
-
Set Clear Goals – decide what you want to achieve, such as reducing downtime or improving product quality.
-
Pick Key Assets – Focus on the machines or systems that are most important to your operations.
-
Build the Right Data System – Use IoT devices and ensure fast data connections for real-time updates.
-
Create the Digital Model – At OEE IntelliSuite, we are working on creating a Digital Twin model for you based on your manufacturing data.
-
Connect with Current Systems – Ensure your digital twins integrate smoothly with your existing systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), which handles tasks like inventory, accounting, and supply chains, and MES (Manufacturing Execution System), which manages and monitors production processes in real-time on the factory floor.
-
Train Your Team – Teach employees how to use and respond to digital twin data.
-
Keep Improving – use feedback and results to constantly refine your digital twin system.
Challenges to Be Aware Of
-
High Initial Costs – Buying sensors, software, and integrating systems can be expensive upfront, though it often pays off later.
-
Security Risks – More connected devices mean more opportunities for cyberattacks, so good security is a must.
-
Technology Integration – Older systems may not connect easily with new ones, requiring extra tools or custom solutions.
-
Skill Gaps – It can be hard to find staff with the proper knowledge in AI, data science, and simulations, so training or hiring is essential.
Examples in the Real World
-
General Electric (GE) – Uses digital twins for engines and turbines to improve reliability and lower maintenance costs.
-
Tesla – Virtual models of its Gigafactories to simulate production workflows, balance energy loads, and streamline line changeovers.
-
Boeing – Uses digital twins to test aircraft systems virtually, saving up to 50% on development costs by catching errors early.
Looking Ahead
As tools like AI, 5G, and edge computing continue to evolve, digital twins will become even more important in manufacturing. Gartner predicts that by 2027, over 70% of industrial companies will use them to improve their operations.
Digital twins aren’t just future tech—they’re already a valuable part of staying competitive in today’s manufacturing world.
Sources
Ignitiv. (2024). Digital twins in manufacturing: The what, why, and how. https://www.ignitiv.com/digital-twins-manufacturing
HyScaler. (2024). Digital twin technology in manufacturing. https://hyscaler.com/insights/digital-twin-technology-manufacturing
Toobler. (2024). Revolutionizing manufacturing with digital twins. https://www.toobler.com/blog/digital-twins-in-manufacturing
DataParc. (2024). Digital twin in manufacturing: What it is & how it’s used. https://www.dataparc.com/blog/digital-twin-manufacturing
McKinsey & Company. (2023). Digital twins: The key to smart product development. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/industrials-and-electronics/our-insights/digital-twins-the-key-to-smart-product-development
Photo By Toobler. (2024). Digital twin & IoT. https://www.toobler.com/blog/digital-twin-iot