Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing: How 3D Printing Is Changing the Way We Create
By: Destiny Dickerson
Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing—better known as 3D printing—is quietly changing the way we design and produce things. From healthcare to construction, this technology is making it easier to create complex, custom, and cost-effective products.
What Is Additive Manufacturing?
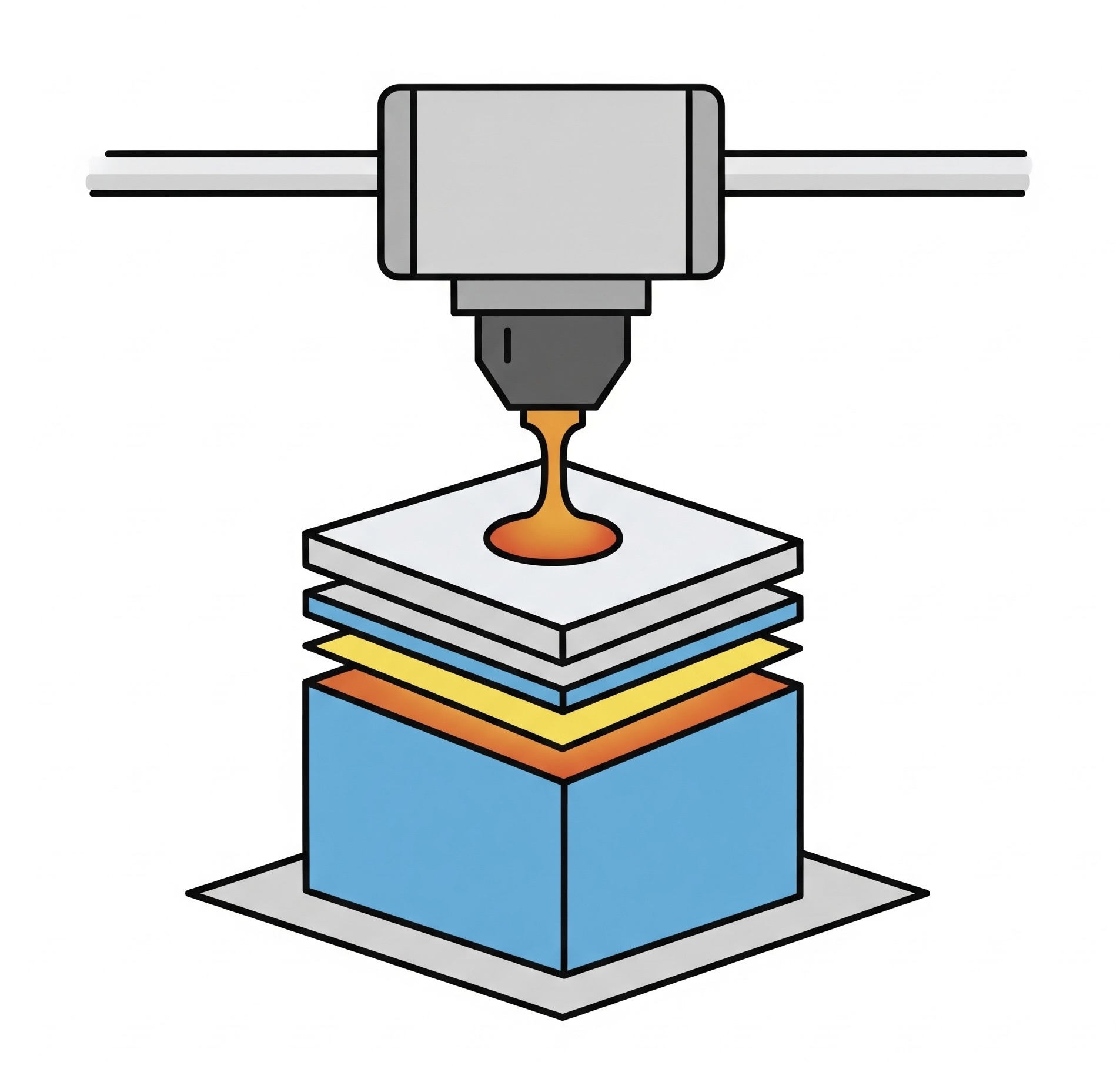
Additive manufacturing is the process of building objects layer by layer using a digital 3D model. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which cuts away at raw materials, additive manufacturing adds only what is needed. This approach saves time, reduces waste, and opens the door to designs that wouldn’t be possible with older methods.
How It Works
The process begins with a digital design, typically created in CAD software. Once the design is complete, it is divided into thin horizontal layers using slicing software. These layers guide the printer as it constructs the object. A 3D printer then lays down material, such as plastic, resin, or metal, layer by layer until the object is complete.
Types of 3D Printing
Fused Deposition Modeling, or FDM, is the most common method, which works by melting a plastic filament to form an object. It’s widely used for basic prototypes. Stereolithography, also known as SLA, utilizes UV light to solidify liquid resin, making it ideal for creating objects with intricate details. Selective Laser Sintering, or SLS, involves using a laser to fuse powdered materials, making it a favorite in industrial design. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) applies the same concept to metal, building strong and durable parts used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Real-World Applications
In healthcare, hospitals and clinics use 3D printing to create custom prosthetics, dental devices, and even surgical tools. Some researchers are exploring ways to print tissue for organ repair, opening up possibilities in regenerative medicine. In the aerospace sector, companies like GE Aviation print engine parts that are lighter and more durable, helping aircraft withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. In the fashion industry, brands such as Adidas and Nike are utilizing 3D printing to create midsoles that mold to an individual’s foot shape, seamlessly blending comfort with style. The automotive industry also benefits from this technology, with manufacturers such as Ford utilizing it for rapid prototyping, which saves time and money during the development process. Even construction is being transformed, as companies like ICON use large-scale 3D printers to build homes in as little as 24 to 48 hours. This innovation offers promising solutions for affordable and emergency housing.
Why It Matters
Additive manufacturing reduces waste and promotes the efficient use of materials. It shortens the time from idea to final product, allowing creators to move from design to prototype in days instead of weeks or months. It supports custom designs at a lower cost, enables on-demand production in small or remote areas, and drives new ideas in healthcare, construction, fashion, and beyond.
Conclusion
Additive manufacturing isn’t just a tool for engineers and designers—it’s becoming an integral part of how we solve problems across various industries. As 3D printing continues to expand, we can expect to see even more creative and meaningful ways it helps improve everyday life.
Sources
- GE Additive. “What is Additive Manufacturing?” https://www.ge.com/additive/additive-manufacturing
- ICON. “3D Printed Homes.” https://www.iconbuild.com/
- Ford Motor Company. “How Ford Uses 3D Printing in Vehicle Development.” https://media.ford.com/
- Adidas. “Futurecraft 4D: The Future of Footwear.” https://www.adidas.com/
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. “3D Printing Medical Devices at the Point of Care.” https://www.fda.gov/
- All3DP. “Types of 3D Printing Explained.” https://all3dp.com/